Page 172 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo quốc tế: Ứng dụng công nghệ mới trong công trình xanh - lần thứ 9 (ATiGB 2024)
P. 172
th
HỘI THẢO QUỐC TẾ ATiGB LẦN THỨ CHÍN - The 9 ATiGB 2024 163
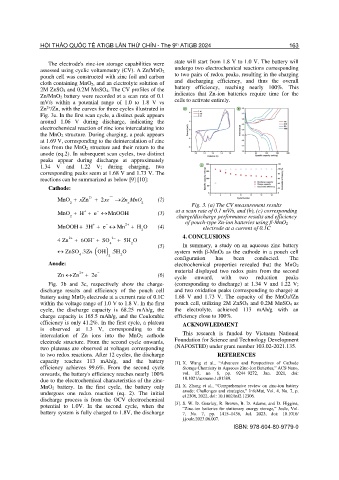
The electrode's zinc-ion storage capabilities were state will start from 1.8 V to 1.0 V. The battery will
assessed using cyclic voltammetry (CV). A Zn/MnO 2 undergo two electrochemical reactions corresponding
pouch cell was constructed with zinc foil and carbon to two pairs of redox peaks, resulting in the charging
cloth containing MnO2, and an electrolyte solution of and discharging efficiency, and thus the overall
2M ZnSO4 and 0.2M MnSO4. The CV profiles of the battery efficiency, reaching nearly 100%. This
Zn/MnO2 battery were recorded at a scan rate of 0.1 indicates that Zn-ion batteries require time for the
mV/s within a potential range of 1.0 to 1.8 V vs cells to activate entirely.
2+
Zn /Zn, with the curves for three cycles illustrated in
Fig. 3a. In the first scan cycle, a distinct peak appears
around 1.06 V during discharge, indicating the
electrochemical reaction of zinc ions intercalating into
the MnO2 structure. During charging, a peak appears
at 1.69 V, corresponding to the deintercalation of zinc
ions from the MnO2 structure and their return to the
anode (eq.2). In subsequent scan cycles, two distinct
peaks appear during discharge at approximately
1.34 V and 1.22 V; during charging, two
corresponding peaks seem at 1.68 V and 1.73 V. The
reactions can be summarized as below [9] [10]:
Cathode:
−
MnO + Zn 2+ + 2xe → Zn MnO (2)
x
2 x 2
Fig. 3. (a) The CV measurement results
−
MnO + H + + e MnOOH (3) at a scan rate of 0.1 mV/s, and (b), (c) corresponding
2 charge/discharge performance results and efficiency
of pouch-type Zn-ion batteries using β-MnO2
+
−
MnOOH 3H + e Mn 2+ + H O (4) electrode at a current of 0.1C
+
2
−
4 Zn 2+ + 6OH + SO 4 2− + 5H O 4. CONCLUSIONS
2
(5) In summary, a study on an aqueous zinc battery
( ) .5H O
ZnSO .3Zn OH system with β-MnO2 as the cathode in a pouch cell
4 2 2
configuration has been conducted. The
Anode: electrochemical properties revealed that the MnO 2
−
Zn Zn 2+ + 2e (6) material displayed two redox pairs from the second
onward,
cycle
peaks
two
reduction
with
Fig. 3b and 3c, respectively show the charge- (corresponding to discharge) at 1.34 V and 1.22 V;
discharge results and efficiency of the pouch cell and two oxidation peaks (corresponding to charge) at
battery using MnO2 electrode at a current rate of 0.1C 1.68 V and 1.73 V. The capacity of the MnO 2//Zn
within the voltage range of 1.0 V to 1.8 V. In the first pouch cell, utilizing 2M ZnSO 4 and 0.2M MnSO4 as
cycle, the discharge capacity is 68.25 mAh/g, the the electrolyte, achieved 113 mAh/g with an
charge capacity is 165.5 mAh/g, and the Coulombic efficiency close to 100%.
efficiency is only 41.2%. In the first cycle, a plateau ACKNOWLEDMENT
is observed at 1.3 V, corresponding to the
intercalation of Zn ions into the MnO 2 cathode This research is funded by Vietnam National
electrode structure. From the second cycle onwards, Foundation for Science and Technology Development
two plateaus are observed at voltages corresponding (NAFOSTED) under grant number 103.02-2021.135.
to two redox reactions. After 12 cycles, the discharge REFERENCES
capacity reaches 113 mAh/g, and the battery [1]. X. Wang et al., “Advances and Perspectives of Cathode
efficiency achieves 99.6%. From the second cycle Storage Chemistry in Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries,” ACS Nano,
onwards, the battery's efficiency reaches nearly 100% vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 9244–9272, Jun. 2021, doi:
due to the electrochemical characteristics of the zinc- 10.1021/acsnano.1c01389.
MnO2 battery. In the first cycle, the battery only [2]. X. Zhang et al., “Comprehensive review on zinc-ion battery
undergoes one redox reaction (eq. 2). The initial anode: Challenges and strategies,” InfoMat, Vol. 4, No. 7, p.
discharge process is from the OCV electrochemical e12306, 2022, doi: 10.1002/inf2.12306.
potential to 1.0V. In the second cycle, when the [3]. S. W. D. Gourley, R. Brown, B. D. Adams, and D. Higgins,
“Zinc-ion batteries for stationary energy storage,” Joule, Vol.
battery system is fully charged to 1.8V, the discharge 7, No. 7, pp. 1415–1436, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.1016/
j.joule.2023.06.007.
ISBN: 978-604-80-9779-0