Page 181 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo quốc tế: Ứng dụng công nghệ mới trong công trình xanh - lần thứ 9 (ATiGB 2024)
P. 181
172 TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC SƯ PHẠM KỸ THUẬT - ĐẠI HỌC ĐÀ NẴNG
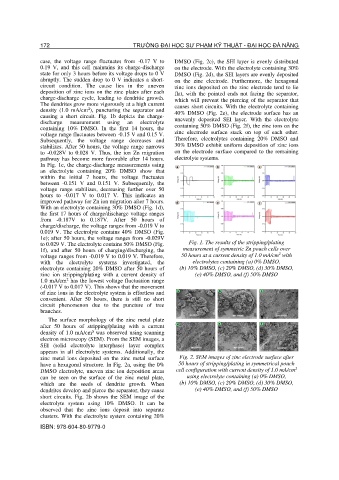
case, the voltage range fluctuates from -0.17 V to DMSO (Fig. 2c), the SEI layer is evenly distributed
0.19 V, and this cell maintains its charge-discharge on the electrode. With the electrolyte containing 30%
state for only 3 hours before its voltage drops to 0 V DMSO (Fig. 2d), the SEI layers are evenly deposited
abruptly. The sudden drop to 0 V indicates a short- on the zinc electrode. Furthermore, the hexagonal
circuit condition. The cause lies in the uneven zinc ions deposited on the zinc electrode tend to lie
deposition of zinc ions on the zinc plates after each flat, with the pointed ends not facing the separator,
charge-discharge cycle, leading to dendritic growth. which will prevent the piercing of the separator that
The dendrites grow more vigorously at a high current causes short circuits. With the electrolyte containing
2
density (1.0 mA/cm ), puncturing the separator and 40% DMSO (Fig. 2e), the electrode surface has an
causing a short circuit. Fig. 1b depicts the charge-
discharge measurement using an electrolyte unevenly deposited SEI layer. With the electrolyte
containing 10% DMSO. In the first 14 hours, the containing 50% DMSO (Fig. 2f), the zinc ions on the
voltage range fluctuates between -0.15 V and 0.15 V. zinc electrode surface stack on top of each other.
Subsequently, the voltage range decreases and Therefore, electrolytes containing 20% DMSO and
stabilizes. After 50 hours, the voltage range narrows 30% DMSO exhibit uniform deposition of zinc ions
to -0.028V to 0.028 V. Thus, the ion Zn migration on the electrode surface compared to the remaining
pathway has become more favorable after 14 hours. electrolyte systems.
In Fig. 1c, the charge-discharge measurements using
an electrolyte containing 20% DMSO show that
within the initial 7 hours, the voltage fluctuates
between -0.151 V and 0.151 V. Subsequently, the
voltage range stabilizes, decreasing further over 50
hours to -0.017 V to 0.017 V. This indicates an
improved pathway for Zn ion migration after 7 hours.
With an electrolyte containing 30% DMSO (Fig. 1d),
the first 17 hours of charge/discharge voltage ranges
from -0.187V to 0.187V. After 50 hours of
charge/discharge, the voltage ranges from -0.019 V to
0.019 V. The electrolyte contains 40% DMSO (Fig.
1e); after 50 hours, the voltage ranges from -0.029V
to 0.029 V. The electrolyte contains 50% DMSO (Fig. Fig. 1. The results of the stripping/plating
1f), and after 50 hours of charging/discharging, the measurement of symmetric Zn pouch cells over
2
voltage ranges from -0.019 V to 0.019 V. Therefore, 50 hours at a current density of 1.0 mA/cm with
with the electrolyte systems investigated, the electrolytes containing (a) 0% DMSO,
electrolyte containing 20% DMSO after 50 hours of (b) 10% DMSO, (c) 20% DMSO, (d) 30% DMSO,
zinc ion stripping/plating with a current density of (e) 40% DMSO, and (f) 50% DMSO
2
1.0 mA/cm has the lowest voltage fluctuation range
(-0.017 V to 0.017 V). This shows that the movement
of zinc ions in the electrolyte system is effortless and
convenient. After 50 hours, there is still no short
circuit phenomenon due to the puncture of tree
branches.
The surface morphology of the zinc metal plate
after 50 hours of stripping/plating with a current
density of 1.0 mA/cm² was observed using scanning
electron microscopy (SEM). From the SEM images, a
SEI (solid electrolyte interphase) layer complex
appears in all electrolyte systems. Additionally, the
zinc metal ions deposited on the zinc metal surface Fig. 2. SEM images of zinc electrode surface after
have a hexagonal structure. In Fig. 2a, using the 0% 50 hours of stripping/plating in symmetrical pouch
2
DMSO electrolyte, uneven zinc ion deposition areas cell configuration with current density of 1.0 mA/cm
can be seen on the surface of the zinc metal plate, using electrolyte containing (a) 0% DMSO,
which are the seeds of dendrite growth. When (b) 10% DMSO, (c) 20% DMSO, (d) 30% DMSO,
dendrites develop and pierce the separator, they cause (e) 40% DMSO, and (f) 50% DMSO
short circuits. Fig. 2b shows the SEM image of the
electrolyte system using 10% DMSO. It can be
observed that the zinc ions deposit into separate
clusters. With the electrolyte system containing 20%
ISBN: 978-604-80-9779-0